2025/01/03
Part 2: Components Of An Electric Linear Actuator
News and Articles
Welcome to Part Two of our six-part series on the fundamentals of electric linear actuators and key considerations when choosing an electric motion system.
If you missed Part One, "What is an Electric Linear Actuator? Definition & Types Explained," we encourage you to explore it. In that installment, we covered the basics of electric linear actuators, including their working principles, various types, and tips for selecting the right actuator for your needs. Don’t miss this essential foundation as we dive deeper into the details in Part Two.
Electric linear actuators are electromechanical devices that transform electrical energy into linear motion, playing a pivotal role in various industries such as healthcare, industrial automation, and home automation. To truly understand how these systems function, diving deep into their components is essential. This article highlights the key electric actuator components, their roles, and how they contribute to the actuator's overall performance.
Benefits of Understanding Electric Actuator Components
Optimized System Design
A deep understanding of electric actuator components allows engineers and designers to choose the ideal actuator for their specific applications. Knowing the strengths, limitations, and compatibility of components such as motors, spindles, and feedback sensors ensures that the actuator will meet operational demands effectively.
Cost Efficiency
Understanding the structure and components of electric actuator components supports better design and contributes to long-term cost savings. Properly chosen components reduce the likelihood of breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the actuator.
Customization Potential
Detailed knowledge of actuator components opens the door to tailored solutions that address unique application requirements. Whether it's integrating a specific type of feedback sensor for precise control or designing a compact housing for limited spaces, customization ensures the actuator seamlessly fits into the system. This flexibility is particularly valuable in industries like robotics or medical equipment, where precision and adaptability are paramount. By understanding component functionalities, manufacturers can collaborate with actuator suppliers to develop bespoke solutions that maximize performance and reliability.
Key Electric Actuator Components and Their Functions
A. Front / Rear Clevis
A clevis is a U-shaped metal piece with holes in each end through which a fastening device, a pin or bolt, is run. Clevis attachments on the front and rear of the actuator allow it to be mounted to the application.
Attachment styles from TiMOTION include round, U-shaped (or slotted), or with a punched hole. TiMOTION can customize clevises to fit best the application in use.
B. Outer Tube
Also known as the cover tube, this extruded aluminum tube protects the outside of the linear actuator and houses all of the actuator's inner components.
C. Inner Tube
The Inner Tube, also known as the extension tube, drive tube, translating tube, or piston, is usually made out of aluminum or stainless steel. While retracted, the inner tube is where the spindle is located. This tube is attached to the threaded drive nut and extends and retracts when the nut moves along the rotating spindle.
D. Spindle
The spindle – also known as the lead screw, rotating screw, or lifting screw – is a long, straight rod that turns into a machine or tool. This linear actuator segment rotates, extending or retracting the nut/inner tube, which creates a linear motion. The spindle can be threaded in different ways for various load and speed capabilities. Additional details of this will be covered in another section.
E. Safety Stop
Positioned at the spindle’s end, the safety stop prevents overextension of the inner tube, ensuring operational safety.
F. Wiper
A wiper seal component is attached to the end of the outer tube, which prevents contaminants like dust and liquids from entering the actuator's spindle area. It also ensures a proper seal between the inner and outer tubes, influencing the linear actuator's IP rating.
TiMOTION's electric linear actuators can be rated anywhere between IP54, IP66, IP67, IP68, and IP69K.
G. Drive Nut
The nut, which can be acme or ball screws, is attached to the inner tube and travels along the spindle. The nut is the component that allows extension or retraction of the inner tube. It can be made of metal or plastic and is sometimes keyed to prevent inner tube rotation.
H. Limit Switches
Limit switches control the fully extended and retracted inner tube position by electrically cutting current to the motor. These switches prevent the actuator from overextending or over-retracting. In addition to cutting current, limit switches can also be used as a signal-sending device.
I. Gear
A gear is made of steel or plastic and mates with other gears to alter the relation between the speed of a driving mechanism (such as the engine of a vehicle) and the speed of the driven parts (the vehicle's wheels). The gear connected to a power source, such as the motor, is called the "drive gear.
J. Motor Housing
The motor housing contains all the internal parts of the gear motor without leaving anything exposed to external damage. TiMOTION's motor housing is typically made of high-quality plastic.
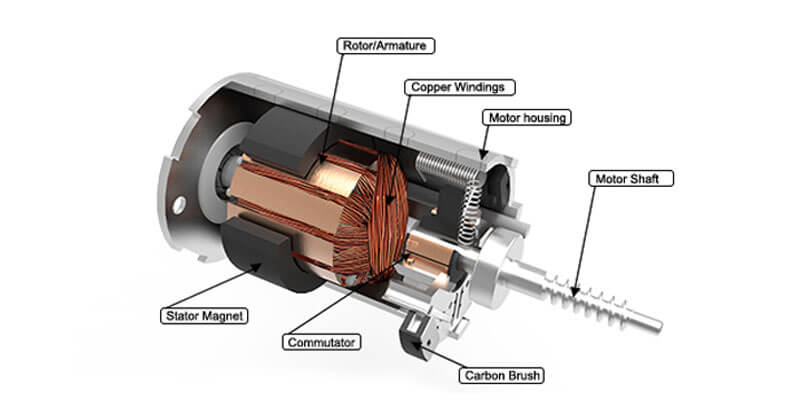
K. DC Motor
The DC (Direct Current) motor is where all of the electric linear actuator's power is generated. There are several types of DC motors, but TiMOTION uses brushed DC motors, which are composed of:
-
Stator
This stationary, outside portion of the motor consists of the motor housing, two permanent magnets, and motor caps. The stator generates a stationary magnetic field that surrounds the rotor.
-
Rotor
The rotor – also known as the armature –is the inner part of the motor that rotates. It mainly consists of silicon steel laminate, motor shaft, commutator, and copper windings.
-
Commutator
The commutator is a pair of plates attached to the motor shaft. These plates provide two connections for the coil of the electromagnet. The commutator is used to reverse the motor's polarity and essentially keeps the motor rotating without losing torque.
-
Carbon Brushes
Carbon brushes use sliding friction to transmit electrical current from the stator to the rotor in the motor.
-
Motor Shaft
The motor shaft connects the gear motor to the bottom of the stator on the DC motor.
Note: Alternating Current Motors (AC Motors) is also an option that TiMOTION manufactures. This type of motor is an available option that can be seen in our MA1 Model.
L. Output/ Feedback Sensors
Output (or feedback) sensors are used to communicate the actuator's stroke position. The feedback that it gives is sent to the control box MCU (micro control unit). Linear actuators with position feedback are typically required when an application involves high-level functions such as synchronization and memory positioning. Output sensor options include:
-
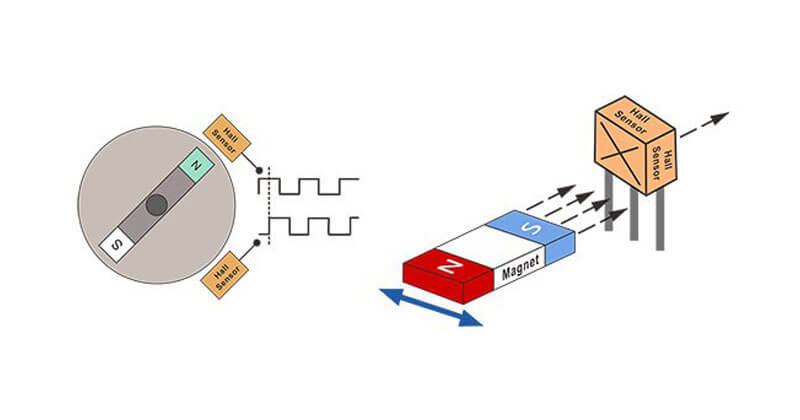
Hall Effect Sensor
The output signal from a Hall Effect sensor is the function of magnetic field density around the device. When the sensor's magnetic flux density exceeds a certain pre-set threshold (set in the MCU), the sensor detects it and generates an output voltage called the Hall Voltage. A linear actuator with position feedback is important because of its reliability and accuracy, which is exactly what the Hall Sensor provides.
-
Potentiometer (POT) Sensor
A POT sensor consists of a wiper/slider and two end connections to change an electrical signal output. As the linear actuator lead screw (spindle) turns, the resistance between the wiper/slider and the two-end connections will change. Each resistance value will correspond to a position in the actuator's stroke.
-
Reed Sensor
The reed sensor is a magnetic positional sensor. It is an electrical switch operated by an applied magnetic field. It consists of a pair of contacts on ferrous metal reeds in a sealed glass envelope. The contacts may be normally open but close when a magnetic field is present (closing the circuit and cutting the actuator's power).
Industry-Specific Component Configurations
Medical Applications
In healthcare, electric actuator components must meet stringent hygiene and precision requirements. Designs with higher water resistance are essential to withstand sterilization chemicals and maintain cleanliness. Integrated feedback sensors enable precise adjustments in applications like hospital beds and surgical tables, ensuring patient comfort and safety. Additionally, electric actuators in medical devices are often designed for quiet operation to minimize noise in sensitive environments.
Industrial Automation
Industrial environments demand heavy-duty actuator components capable of withstanding intense force and harsh conditions. High-strength steel spindles, robust motor housings, and advanced sealing solutions protect against dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. Feedback sensors provide real-time data for monitoring and controlling machinery in applications such as conveyor belts and robotic arms. Durability and reliability are key, as actuators in these settings must perform consistently under heavy loads and repetitive cycles.
Electric Actuator Testing Standards
Electric actuators undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet rigorous industry standards for performance, reliability, and safety. These tests are designed to validate the actuator's functionality across various applications and operating conditions:
Performance
Electric actuators are evaluated for load capacity, speed, and precision under different environmental and operational scenarios. These tests confirm that the actuator can consistently meet its specified capabilities without compromising functionality.
Reliability
Stress tests simulate prolonged use to assess wear and tear on critical components such as motors, gears, and spindles. This testing ensures the durability of the actuator and minimizes maintenance requirements, making it suitable for long-term applications.
Safety
Safety testing focuses on critical features like overload protection, proper operation of limit switches, and adherence to IP ratings for resistance to water, dust, and other contaminants. These evaluations are essential for applications in healthcare, industrial automation, and other settings where reliability and safety are paramount.
Understanding the components of an electric linear actuator is the first step toward optimizing your applications. We hope that this article has helped you develop a better understanding and foundation for electric linear actuators.
Next, we will cover the safety feature options that can be added to an actuator.
TiMOTION offers customizable, high-quality solutions tailored to meet diverse needs. Whether you’re looking for precision, durability, or advanced feedback systems, TiMOTION has the expertise to assist.
Contact us today to explore how our electric actuator components can elevate your systems to the next level.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What role do feedback sensors play in electric actuators?
A: Feedback sensors provide critical data about the actuator's stroke position, ensuring precise control. They are particularly useful in applications requiring synchronization or memory positioning.
Q2: How does the wiper enhance actuator durability?
A: The wiper seals the spindle area, preventing contaminants from entering and ensuring smooth operation. It also determines the actuator’s IP rating, which is critical for applications in harsh environments.
Q3: Why are limit switches essential?
A: Limit switches prevent overextension or over-retraction of the actuator, protecting both the actuator and the application. They also enhance automation by signaling control systems.















